Гидроксизин канон
Содержание:
- Stability
- Usual Adult Dose for Anxiety
- Hydroxyzine Capsules — Clinical Pharmacology
- Спасение от передозировки
- Uses for Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride
- Precautions
- Usual Pediatric Dose for Pruritus
- What other drugs will affect hydroxyzine?
- Фармакокинетика
- How should I take hydroxyzine?
- How is Hydroxyzine Capsules Supplied
- Аналоги
- Hydroxyzine side effects
- Adverse Reactions
- Actions
- Hydroxyzine Capsules Description
- Contraindications
- Adverse Reactions
- Побочные эффекты
- Противопоказания
- Лекарственное взаимодействие
- Overdosage
- Hydroxyzine — Clinical Pharmacology
Stability
Storage
Oral
Tight, light-resistant containers at ≤40°C (preferably 15–30°C). Avoid freezing.
Injection
b Avoid freezing.
Compatibility
For information on systemic interactions resulting from concomitant use, see Interactions.
|
Compatible |
|---|
|
Atropine sulfate |
|
Buprenorphine HCl |
|
Butorphanol tartrate |
|
Chlorpromazine HCl |
|
Diphenhydramine HCl |
|
Doxapram HCl |
|
Droperidol |
|
Fentanyl citrate |
|
Fluphenazine HCl |
|
Glycopyrrolate |
|
Hydromorphone HCl |
|
Lidocaine HCl |
|
Meperidine HCl |
|
Metoclopramide HCl |
|
Midazolam HCl |
|
Morphine sulfate |
|
Nalbuphine HCl |
|
Pentazocine lactate |
|
Prochlorperazine edisylate |
|
Promethazine HCl |
|
Scopolamine HBr |
|
Incompatible |
|
Dimenhydrinate |
|
Haloperidol lactate |
|
Ketorolac tromethamine |
|
Pentobarbital sodium |
|
Ranitidine HCl |
Usual Adult Dose for Anxiety
Oral: 50 to 100 mg orally 4 times a day
Parenteral: 50 to 100 mg IM immediately, then every 4 to 6 hours as neededComments:
-Use should be periodically reassessed.
-Treatment for longer than 4 months have not been assessed in clinical studies.Uses:Oral:
-As an adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested
-Symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosisParenteral:
-Adjunctive treatment in alcoholism
-Allay associated anxiety and apprehension attendant to certain types of heart disease
-Alleviating anxiety and tension in acute emotional problems or in the preparation for dental procedures
-As pre-/postoperative and pre-/postpartum adjunctive medication to allay anxiety
-Management of anxiety associated with allergic conditions with strong emotional overlay (e.g., asthma, chronic urticaria, pruritus)
-Management of anxiety associated with organic disturbances
-Treatment of patients who are acutely/chronically alcoholic with anxiety withdrawal symptoms or delirium tremens
-Treatment of patients who are acutely disturbed or hysterical
Hydroxyzine Capsules — Clinical Pharmacology
Hydroxyzine pamoate is unrelated chemically to the phenothiazines, reserpine, meprobamate, or the benzodiazepines.
Hydroxyzine pamoate is not a cortical depressant, but its action may be due to a suppression of activity in certain key regions of the subcortical area of the central nervous system. Primary skeletal muscle relaxation has been demonstrated experimentally. Bronchodilator activity, and antihistaminic and analgesic effects have been demonstrated experimentally and confirmed clinically. An antiemetic effect, both by the apomorphine test and the veriloid test, has been demonstrated. Pharmacological and clinical studies indicate that hydroxyzine in therapeutic dosage does not increase gastric secretion or acidity and in most cases has mild antisecretory activity. Hydroxyzine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and hydroxyzine pamoate’s clinical effects are usually noted within 15 to 30 minutes after oral administration.
Спасение от передозировки
Беспокоиться нужно при возникновении таких симптомов:
- Тошнота и рвота.
- Гипертермия.
- Тахикардия.
- Сонливость.
- Тремор.
- Нарушение зрачкового рефлекса.
- Галлюцинации и спутанность сознания.
- Судороги.
- Угнетение дыхания и сознания.
- Низкое артериальное давление.
- Аритмия.
- Сердечно-легочный коллапс и усугубление коматозного состояния.
Спасение человека в результате передозировки включает в себя следующие меры:
- Контроль состояния дыхательных путей и кровообращения.
- Проведение электрокардиографического мониторинга.
- Обеспечение хорошей оксигенации.
- Контроль давления и сердечной деятельности в течение 24 часов после прохождения симптомов.
Важно быть готовым к нарушению психического статуса. Пациент должен отказаться от алкоголя и других препаратов
Возможно, понадобится проведение кислородной ингаляции, а также введение налоксона, декстрозы и тиамина. Но ни в коем случае нельзя применять аналептики – это запрещено.

Если же врач считает необходимым оказание вазопрессорного действия, пациенту назначают метараминол или норэпинефрин. Эпинефрин не принимают.
Можно еще выполнить промывание желудка, которому обязательно должна предшествовать эндотрахеальная интубация. Касательно активированного угля, его можно принять, но данных, подтверждающих его эффективность, очень мало. Специфического антидота нет, а гемодиализ просто неэффективен.
Также в некоторых источниках указано, что в случае реальной угрозы для жизни допускается использование физостигмина. Это опасное средство – если человек употреблял трициклические антидепрессанты, то оно может привести к судорожным приступам или необратимой остановке сердца.
Uses for Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride
Anxiety
Symptomatic management of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneuroses and as an adjunct in patients with organic disease states who have associated anxiety; however, most clinicians consider other anxiolytic agents (e.g., benzodiazepines) more effective.
Has been used to allay anxiety in prepartum and postpartum states.
Has been used for prompt control of acutely disturbed or hysterical patients.
Pruritus
Management of pruritus caused by allergic conditions (e.g., chronic urticaria, atopic or contact dermatoses) and in histamine-mediated pruritus.
Sedation before and after general anesthesia.
Has been used to reduce opiate analgesic requirements.
Nausea and Vomiting
Management of nausea and vomiting of various etiologies (e.g., postoperative).
Safety for prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy not established; contraindicated during early pregnancy.
Precautions
THE POTENTIATING ACTION OF Hydroxyzine MUST BE CONSIDERED WHEN THE DRUG IS USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM DEPRESSANTS SUCH AS NARCOTICS, NON-NARCOTIC ANALGESICS AND BARBITURATES. Therefore, when central nervous system depressants are administered concomitantly with Hydroxyzine, their dosage should be reduced. Since drowsiness may occur with use of the drug, patients should be warned of this possibility and cautioned against driving a car or operating dangerous machinery while taking Hydroxyzine pamoate. Patients should be advised against the simultaneous use of other CNS depressant drugs, and cautioned that the effect of alcohol may be increased.
QT Prolongation/Torsade de Pointes (TdP): Cases of QT prolongation and Torsade de Pointes have been reported during post-marketing use of Hydroxyzine. The majority of reports occurred in patients with other risk factors for QT prolongation/TdP (pre-existing heart disease, electrolyte imbalances or concomitant arrhythmogenic drug use). Therefore, Hydroxyzine should be used with caution in patients with risk factors for QT prolongation, congenital long QT syndrome, a family history of long QT syndrome, other conditions that predispose to QT prolongation and ventricular arrhythmia, as well as recent myocardial infarction, uncompensated heart failure, and bradyarrhythmias.
Caution is recommended during the concomitant use of drugs known to prolong the QT interval. These include Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmics, certain antipsychotics (e.g., ziprasidone, iloperidone, clozapine, quetiapine, chlorpromazine), certain antidepressants (e.g., citalopram, fluoxetine), certain antibiotics (e.g., azithromycin, erythromycin, clarithromycin, gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin); and others (e.g., pentamidine, methadone, ondansetron, droperidol).
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP): Hydroxyzine may rarely cause acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), a serious skin reaction characterized by fever and numerous small, superficial, non-follicular, sterile pustules, arising within large areas of edematous erythema. Inform patients about the signs of AGEP, and discontinue Hydroxyzine at the first appearance of a skin rash, worsening of pre-existing skin reactions which Hydroxyzine may be used to treat, or any other sign of hypersensitivity. If signs or symptoms suggest AGEP, use of Hydroxyzine should not be resumed and alternative therapy should be considered. Avoid cetirizine or levocetirizine in patients who have experienced AGEP or other hypersensitivity reactions with Hydroxyzine, due to the risk of cross-sensitivity.
Geriatric Use
A determination has not been made whether controlled clinical studies of Hydroxyzine pamoate included sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to define a difference in response from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
The extent of renal excretion of Hydroxyzine pamoate has not been determined. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selections. Sedating drugs may cause confusion and over sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of Hydroxyzine pamoate and observed closely.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Pruritus
Children:
-Under 6 years: 50 mg orally per day, given in divided doses
-Over 6 years: 50 to 100 mg orally per day, given in divided dosesUses:
-Allay associated anxiety and apprehension attendant to certain types of heart disease
-Alleviating anxiety and tension in acute emotional problems or in the preparation for dental procedures
-As pre-/postoperative and pre-/postpartum adjunctive medication to allay anxiety
-Management of anxiety associated with allergic conditions with strong emotional overlay (e.g., asthma, chronic urticaria, pruritus)
-Management of anxiety associated with organic disturbances
-Management of pruritus due to histamine-mediated pruritus and allergic conditions (e.g., atopic/contact dermatoses, chronic urticaria)
-Treatment of patients who are acutely disturbed or hysterical
What other drugs will affect hydroxyzine?
Taking this medicine with other drugs that make you sleepy can worsen this effect. Ask your doctor before taking hydroxyzine with a sleeping pill, narcotic pain medicine, muscle relaxer, or medicine for anxiety, depression, or seizures.
Hydroxyzine can cause a serious heart problem, especially if you use certain medicines at the same time, including antibiotics, antidepressants, heart rhythm medicine, antipsychotic medicines, and medicines to treat cancer, malaria, HIV or AIDS. Tell your doctor about all medicines you use, and those you start or stop using during your treatment with this medicine.
Other drugs may interact with hydroxyzine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible interactions are listed here. Tell each of your health care providers about all medicines you use now and any medicine you start or stop using.
Фармакокинетика
О ней также нужно рассказать, изучая инструкцию по применению «Гидроксизина Канон». Действующее вещество очень хорошо усваивается организмом. Своей максимальной концентрации оно достигает через два часа после применения.
Если говорить о коэффициенте распределения, то он у взрослых равен 7-16 л/кг
Важно знать, что вещество проникает через плаценту и гематоэнцефалический барьер, хотя и концентрируется он больше не в материнских тканях, а в фетальных
Седативное средство отлично проникает в кожу – в ней его концентрация оказывается намного выше, чем в сыворотке крови. Поэтому оно способно устранить многие воспаления.
Метаболизируется вещество в печени. Главным метаболитом (45 %) является цетиризин – это тоже блокатор Н1-гистаминовых рецепторов. Он, как и многие другие продукты распада, проникает в грудное молоко.
Период полураспада препарата «Гидроксизин Канон» длится в среднем 14 часов. Но диапазон намного больше – от 7 до 20 час. Общий клиренс равен 13 мл/мин/кг. Всего лишь 0,8 % вещества покидает организм через почки в неизменном виде. Основной метаболит выводится с мочой.
У пожилых пациентов период полураспада может длиться 29 часов. Поэтому им, как правило, препарат назначают в меньшей дозировке. Детям дозу также корректируют, ведь у них период полураспада составляет всего 4 часа, а клиренс в 2,5 раза превышает взрослый.
Особую схему приема назначают пациентам, имеющим проблемы с печенью. Ведь у них период полураспада может достигать 37 часов, а общий клиренс составлять 66 %. И концентрация метаболитов в сыворотке крови выше.
Касательно пациентов с почечной недостаточностью, в результате наблюдения за ними удалось выяснить, что у них увеличивается длительность экспозиции цетиризина. Интересно, что длительность экспозиции гидроксизина при этом не изменилась
Потому таким пациентам дозировка также подбирается с осторожностью
How should I take hydroxyzine?
Take hydroxyzine exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose. Do not use this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
Shake the oral suspension (liquid) well just before you measure a dose. Measure liquid medicine with the dosing syringe provided, or with a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup. If you do not have a dose-measuring device, ask your pharmacist for one.
Hydroxyzine is for short-term use only.
You should not take this medicine for longer than 4 months. Call your doctor if your anxiety symptoms do not improve, or if they get worse.
Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
How is Hydroxyzine Capsules Supplied
Hydroxyzine Pamoate Capsules (hydroxyzine pamoate equivalent to hydroxyzine hydrochloride) are available as:
25 mg capsules: Hard gelatin capsules, green opaque cap, green opaque body, cap and body imprinted EP136 in black ink. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC 14539-674-01
Bottles of 500: NDC 14539-674-05
50 mg capsules: Hard gelatin capsules, white opaque cap, green opaque body, cap and body imprinted EP112 in black ink. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC 14539-675-01
Bottles of 500: NDC 14539-675-05
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) .
Dispense in tight, light resistant containers (USP).
Manufactured by:
Heritage Pharma Labs Inc.
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
1.866.901.DRUG (3784)
51U000000293US03
Revised: 04/2019
Аналоги
У рассматриваемого медикамента есть известная альтернатива, и люди, зная об этом, задаются вопросом: что лучше – «Гидроксизин Канон» или «Атаракс»?
Оба средства – это транквилизаторы, применяемые в терапии тревожных расстройств. Каждое из них отличается оптимальным соотношением безопасности и эффективности. По составу и механизму действия они также одинаковы.
Еще из аналогов, похожих как на первый препарат, так и на второй, можно отметить вниманием «Валерианахель», «Селанк», «Клопиксол-акуфаз», «Афобазол», «Золофт», «Элзепам», «Ципралекс», «Стрезам», «Паглюферал», а также «Адаптол». Из мощнейших препаратов можно выделить «Феназепам»
Он помогает справиться даже с такими серьезными состояниями, как невроз, эпилептические приступы, психомоторное возбуждение. Он даже устраняет хронические боли
Из мощнейших препаратов можно выделить «Феназепам». Он помогает справиться даже с такими серьезными состояниями, как невроз, эпилептические приступы, психомоторное возбуждение. Он даже устраняет хронические боли.

Но помните: даже если «Гидроксизин Канон» не получается по каким-то причинам найти в аптеке, подбирать альтернативу необходимо только вместе с врачом.
Hydroxyzine side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to hydroxyzine: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
In rare cases, hydroxyzine may cause a severe skin reaction. Stop taking this medicine and call your doctor right away if you have sudden skin redness or a rash that spreads and causes white or yellow pustules, blistering, or peeling.
Stop using hydroxyzine and call your doctor at once if you have:
-
fast or pounding heartbeats;
-
headache with chest pain;
-
severe dizziness, fainting; or
-
a seizure (convulsions).
Side effects such as drowsiness and confusion may be more likely in older adults.
Common hydroxyzine side effects may include:
-
drowsiness;
-
headache;
-
dry mouth; or
-
skin rash.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Adverse Reactions
Side effects reported with the administration of Hydroxyzine pamoate are usually mild and transitory in nature.
Skin and Appendages: Oral Hydroxyzine hydrochloride is associated with Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP) and fixed drug eruptions in post-marketing reports.
Anticholinergic: Dry mouth.
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness is usually transitory and may disappear in a few days of continued therapy or upon reduction of the dose. Involuntary motor activity, including rare instances of tremor and convulsions, has been reported, usually with doses considerably higher than those recommended. Clinically significant respiratory depression has not been reported at recommended doses.
Cardiac System: QT prolongation,Torsade de Pointes.
In post-marketing experience, the following additional undesirable effects have been reported: Body as a Whole: allergic reaction, Nervous System: headache, Psychiatric: hallucination, Skin and Appendages: pruritus, rash, urticaria.
Actions
-
Exhibits antihistaminic, CNS depressant, anticholinergic, antispasmodic, local anesthetic activity, analgesic, sedative and antiemetic activity. Also exhibits primary skeletal muscle relaxant activity.
-
Sedative and tranquilizing effects result principally from suppression of activity at subcortical levels of the CNS.
-
Antispasmodic activity apparently mediated through interference with the mechanism that responds to spasmogenic agents such as acetylcholine, histamine, and serotonin.
-
Antiemetic and antimotion sickness actions may result at least in part from central anticholinergic and CNS depressant properties.
Hydroxyzine Capsules Description
Hydroxyzine pamoate is a light yellow odorless powder, practically insoluble in water and methanol and freely soluble in dimethylformamide. It is chemically designated as (±)-2-ethoxy]ethanol 4,4 -methylenebis (1:1) and can be structurally represented as follows:
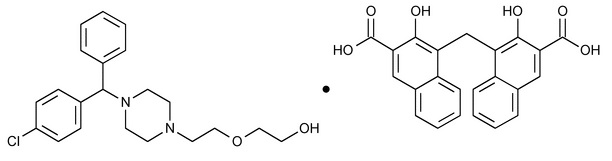
Chemical Formula: C21H27ClN2O2.C23H16O6
Molecular Weight: 763.29
Inert ingredients for the capsule formulations are: hard gelatin capsules (which contain gelatin, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40, D&C Yellow #10), printing ink which contains shellac glaze ~45% (20% esterified) in Ethanol, iron oxide black, n-butyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, propylene glycol and ammonium hydroxide 28%); magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch glycolate.
Contraindications
Hydroxyzine, when administered to the pregnant mouse, rat, and rabbit, induced fetal abnormalities in the rat and mouse at doses substantially above the human therapeutic range. Clinical data in human beings are inadequate to establish safety in early pregnancy. Until such data are available, hydroxyzine is contraindicated in early pregnancy.
Hydroxyzine is contraindicated in patients with a prolonged QT interval.
Hydroxyzine pamoate is contraindicated for patients who have shown a previous hypersensitivity to any component of this medication.
Hydroxyzine is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to hydroxyzine products, and in patients with known hypersensitivity to cetirizine hydrochloride or levocetirizine hydrochloride.
Adverse Reactions
Side effects reported with the administration of hydroxyzine pamoate are usually mild and transitory in nature.
Skin and Appendages: Oral hydroxyzine hydrochloride is associated with Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP) and fixed drug eruptions in post-marketing reports.
Anticholinergic: Dry mouth.
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness is usually transitory and may disappear in a few days of continued therapy or upon reduction of the dose. Involuntary motor activity, including rare instances of tremor and convulsions, has been reported, usually with doses considerably higher than those recommended. Clinically significant respiratory depression has not been reported at recommended doses.
Cardiac System: QT prolongation, Torsade de Pointes.
In post-marketing experience, the following additional undesirable effects have been reported: Body as a Whole: allergic reaction, Nervous System: headache, Psychiatric: hallucination, Skin and Appendages: pruritus, rash, urticaria.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Heritage Pharmaceuticals at 1-866-901-DRUG (3784) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Побочные эффекты
Обсудив фармакологическое действие «Гидроксизина Канон», необходимо немного внимания уделить и нежелательным реакциям. Они могут возникнуть, если начать принимать препарат не по назначению и без консультации врача. Вот какие последствия случаются:
- Иммунная система: анафилактический шок, гиперчувствительность.
- ЦНС: тремор, бессонница, головокружение, дискинезия, судороги, спутанность сознания, дезориентация, возбужденность, галлюцинации.
- Дыхательная система: бронхоспазмы.
- Почки и мочевыводящие пути: задержка мочеиспускания.
- Органы зрения: проблемы с четкостью восприятия, нарушение аккомодации.
- ЖКТ: запоры, рвота, тошнота.
- Сердечно-сосудистая система: тахикардия, удлинение на электрокардиограмме интервала QT, желудочковая тахикардия, понижение артериального давления.
- Желчевыводящие пути и печень: гепатит, нарушение функциональных проб.
- Кожа: макулопапулезная и эритематозная сыпь, зуд, дерматит, крапивница, повышенная потливость, ангионевротический отек, острое высыпание, синдром Стивенса — Джонсона, многоформная эритема.

Также часто пациенты сталкиваются с недомоганием и гипертермией. Еще может развиться тромбоцитопения, депрессия, агрессия, парестезия, дистония, нервный тик, окулогирный криз, дизурия, отеки, астения, энурез и т. д.
Противопоказания
Основными показаниями к применению таблетированного фармакологического средства Гидроксизин выступают следующие состояния пациента:
- Необходимость устранить чрезмерную тревожность и завышенную возбудимость нервной системы.
- В качестве средства, облегчающего состояние пациента в случае алкогольной абстиненции.
- При наличии у пациента ряда психоневротических расстройств.
- В рамках комплексной терапии после перенесенных хирургических вмешательств и некоторого ряда травм.
- Как средство для премедикации.
- При скопившемся внутреннем перенапряжении, расстройствах адаптивных способностей, заболеваниях соматического характера и генерализованной тревоге.
- Для ликвидации симптоматики в случае зудящего дерматоза, дерматите атопическом, экземе и крапивнице.
- По показаниям как противорвотный медикамент.
У Гидроксизина имеется определенный ряд противопоказаний, при наличии которые применять препарат не рекомендуется:
- при наличии глаукомы у пациента;
- в случае гипертрофии предстательной железы;
- при повышенной судорожной активности пациента;
- в случае миастении;
- при недостаточности почек;
- в случае печеночной недостаточности;
- в период беременности;
- в ходе лактации;
- при деменции;
- в случае порфирии;
- в случае аллергической реакции на компоненты медикамента;
- в ходе родовой деятельности.
Гидроксизин назначают в качестве антигистаминного медпрепарата, а также в качестве анальгезирующего и седативного лекарства. Основное использование медпрепарата при таких патологиях:
- тревожное состояние;
- психомоторное перевозбуждение;
- внутреннее перенапряжение;
- нарушение процесса адаптации;
- раздражительность и повышенная нервозность;
- абстинентный синдром алкогольной этиологии;
- премедикация после оперативного лечения;
- аллергической этиологии зуд;
- дерматиты;
- кожные экземы.
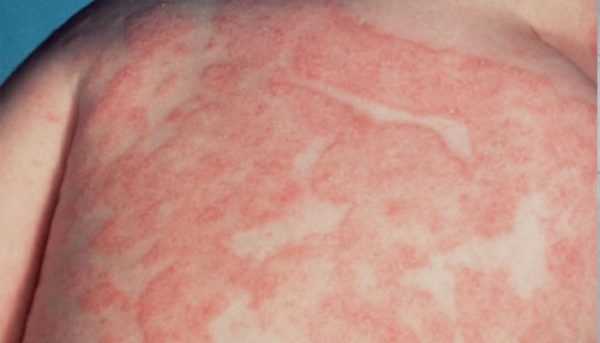
Экзема
Не назначают медпрепарат при таких патологиях у пациента:
- аллергия на компоненты в составе лекарства;
- порфирия;
- непереносимость лактозы;
- дефицит Лаппа.
С высокой осторожностью используют Гидроксизин при таких сопутствующих болезнях у пациента:
- миастения;
- сердечная недостаточность;
- аритмия;
- деменция;
- нарушение в мочеиспускании и постоянные запоры;
- эпилепсия и гипертензия;
- гипокалиемия и гипомагниемия;
- глаукома;
- гипертиреоз;
- патологии органов ЖКТ.
Лекарственное взаимодействие
«Гидроксизин Канон» может вступать в различные химические реакции с другими медикаментами. Вот как он может взаимодействовать с иными препаратами:
- Сочетаясь с наркотическими анальгетиками, алкоголем, снотворными средствами, транквилизаторами и барбитуратами, гидроксизин оказывает потенцирующее действие.
- Одновременно с холиноблокаторами и ингибиторами моноаминооксидазы пить это средство не стоит. Ибо оно препятствует противосудорожной активности фенитоина, прессорному действию эпинефрина, ингибиторов холинэстеразы и бетагистина.
- Циметидин может увеличивать концентрацию гидроксизина в сыворотке крови примерно на 36 %. А вот максимальная концентрация метаболита уменьшается на 20 %.
- В высоких дозах гидроксизин может взаимодействовать с субстратами CYP2D6.
- Концентрация данного вещества в плазме крови может быть увеличена из-за его одновременного употребления с препаратами, которые ингибируют изофермент CYP3A4/5. Это телитромицин, нелфинавир, атазанавир, делавирдин, типранавир и еще десятки иных препаратов.
- Если одновременно употреблять данное средство с ингибиторами микросомальных ферментов печени, то следует ожидать увеличения концентрация гидроксизина в плазме крови.
- Медикаменты, отличающиеся ототоксическим действием (гентамицин, например), могут маскировать некоторые признаки отравления, например головокружение.
К слову, хранить таблетки надо в темном месте, где температура не превышает 25 °С. И разумеется, там, куда не доберутся дети. Срок годности ограничен двумя годами.
Overdosage
The most common manifestation of overdosage of hydroxyzine pamoate is hypersedation. Other reported signs and symptoms were convulsions, stupor, nausea and vomiting. As in the management of overdosage with any drug, it should be borne in mind that multiple agents may have been taken.
If vomiting has not occurred spontaneously, it should be induced. Immediate gastric lavage is also recommended. General supportive care, including frequent monitoring of the vital signs and close observation of the patient, is indicated. Hypotension, though unlikely, may be controlled with intravenous fluids and vasopressors (do not use epinephrine as hydroxyzine counteracts its pressor action.) Caffeine and Sodium Benzoate Injection, USP, may be used to counteract central nervous system depressant effects.
Hydroxyzine overdose may cause QT prolongation and Torsade de Pointes. ECG monitoring is recommended in cases of hydroxyzine overdose.
There is no specific antidote. It is doubtful that hemodialysis would be of any value in the treatment of overdosage with hydroxyzine. However, if other agents such as barbiturates have been ingested concomitantly, hemodialysis may be indicated. There is no practical method to quantitate hydroxyzine in body fluids or tissue after its ingestion or administration.
DOSAGE
For symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosis and as an adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested: in adults, 50–100 mg q.i.d.; children under 6 years, 50 mg daily in divided doses; and over 6 years, 50–100 mg daily in divided doses.
For use in the management of pruritus due to allergic conditions such as chronic urticaria and atopic and contact dermatoses, and in histamine-mediated pruritus: in adults, 25 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d.; children under 6 years, 50 mg daily in divided doses; and over 6 years, 50–100 mg daily in divided doses.
As a sedative when used as a premedication and following general anesthesia: 50–100 mg in adults, and 0.6 mg/kg in children.
When treatment is initiated by the intramuscular route of administration, subsequent doses may be administered orally.
As with all medications, the dosage should be adjusted according to the patient’s response to therapy.
Hydroxyzine — Clinical Pharmacology
Hydroxyzine pamoate is unrelated chemically to the phenothiazines, reserpine, meprobamate, or the benzodiazepines. Hydroxyzine pamoate is not a cortical depressant, but its action may be due to a suppression of activity in certain key regions of the subcortical area of the central nervous system. Primary skeletal muscle relaxation has been demonstrated experimentally. Bronchodilator activity, and antihistaminic and analgesic effects have been demonstrated experimentally and confirmed clinically. An antiemetic effect, both by the apomorphine test and the veriloid test, has been demonstrated. Pharmacological and clinical studies indicate that Hydroxyzine in therapeutic dosage does not increase gastric secretion or acidity and in most cases has mild antisecretory activity. Hydroxyzine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and Hydroxyzine pamoate’s clinical effects are usually noted within 15 to 30 minutes after oral administration.